Autonomous EV Showcases Polycarbonate Glazing, Doors
Teijin and Applied Electric Vehicles have teamed up to develop an energy-efficient, low-speed EV that consumes roughly the same amount of energy as a pedestrian.
March 31, 2021
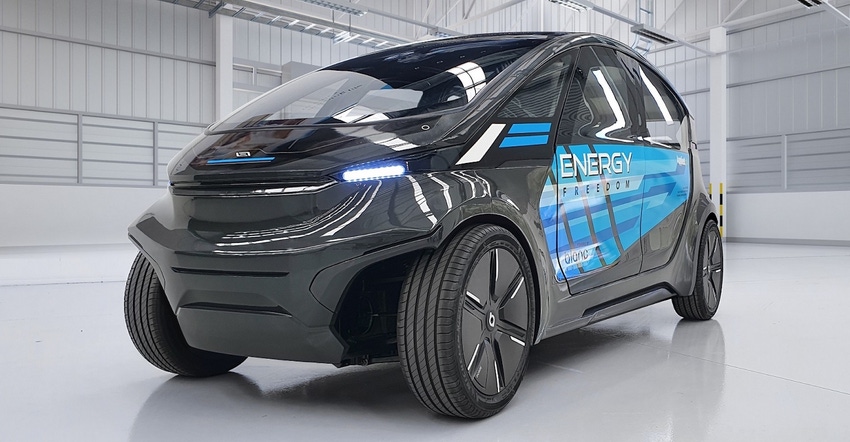

Teijin Ltd. and Applied Electric Vehicles (Applied EV) have teamed up to develop an energy-efficient, low-speed electric vehicle (LS-EV) prototype for autonomous driving systems and other applications that are expected to help realize zero-emission mobility.
The four-seat LS-EV embodies a well-to-wheel zero-emission approach that combines Teijin’s expertise in strong, lightweight materials and processing and molding technologies and Applied EV’s new mobility vehicle platform. Called Blanc Robot, the platform is built entirely from first principles, integrating a new high-efficiency driveline and full drive-by-wire technologies.
Built on the Blanc Robot zero-emission platform, the vehicle incorporates Teijin's materials and technical know-how. It achieves unprecedented energy efficiency for an autonomous vehicle, consuming roughly the same amount of energy as a pedestrian. It can also be used for autonomous driving systems.
Curved roof fitted with solar panel
Teijin’s lightweight, impact-resistant Panlite polycarbonate resin glazing is used for the windows and doors — the vehicle’s main components — enabling the stylish body. Polycarbonate used for the prototype also provides excellent infrared blocking and helps moderate temperatures in the cabin interior.
The curved roof, which has been integrally molded with a Panlite glazing, is fitted with a solar panel and lightweight power supply module. The system achieves output of about 330 W, which is equivalent to a conventional solar panel housed under glass.
The field of mobility is undergoing significant transformation propelled by new concepts such as connected, autonomous, shared, and electric (CASE) vehicles and mobility as a service (MaaS). Electrification and autonomous technologies are rapidly being developed for next-generation mobility applications that will help to reduce environmental impact and address new needs in society, such as transportation for aging societies.
Well-to-wheel zero-emission technology
The shift to electric mobility is focusing attention on the benefit of the well-to-wheel zero-emission approach, which takes into account the total energy efficiency of vehicles, including how their electricity is sourced and how efficiently it is used during driving. Teijin and Applied EV, which commenced their joint-development collaboration in 2019, are committed to establishing a technological foundation for supporting practical, multipurpose zero-emission vehicles in future society.
“A focus on sustainable solutions can be very good for business economics,” said Julian Broadbent, CEO of Applied EV. “By working in collaboration with Teijin, reducing the mass of an entire vehicle, one requires less energy for a given task and, therefore, less battery size. As a net result, with a similar roof area as a traditional vehicle, we find solar technology makes very good sense with real world impacts and a very nice business case.”
Toshiaki Hotaka, General Manager of Teijin Ltd.’s Mobility Division, said: “Through our collaboration with Applied EV, we are working to realize well-to-wheel zero-emission solutions that anticipate mobility needs in the near future. To this end, we are strengthening our technological capabilities by applying our know-how in high-performance materials, design, and composites. Aiming to become a company that supports the society of the future, we have positioned environmental-value solutions as a priority field in which Teijin can contribute to circular economies and sustainability.”
About the Author(s)
You May Also Like